Niels Bohr
“If anybody says he can think about quantum physics without getting giddy, that only shows he has not understood the first thing about them.”
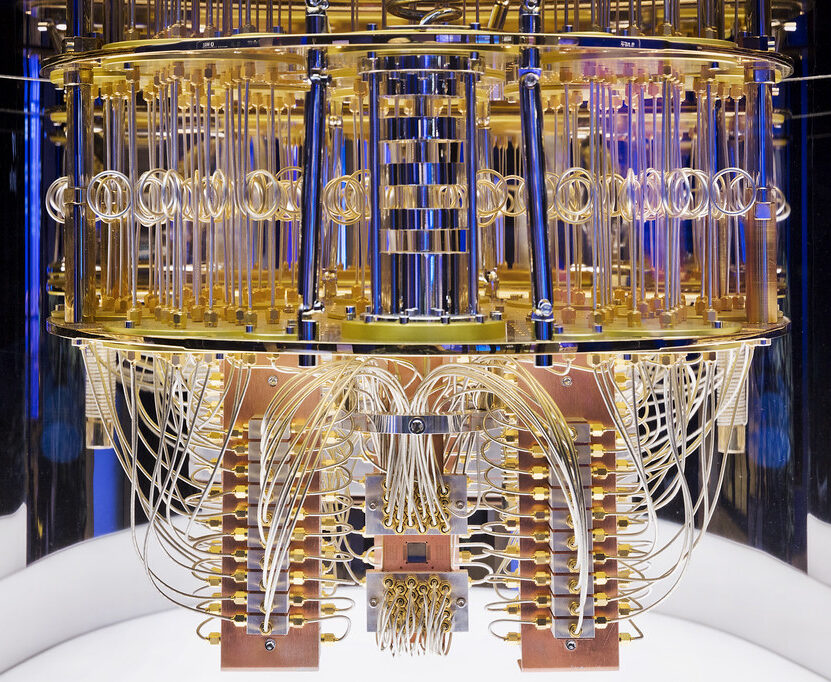
Recently, quantum computing has shown immense growth, turning into its own field from just a theoretical concept. It promises to change a lot of industries drastically, including cryptography. Classical computers process information in binary (0s and 1s), where as quantum computers use the principles of quantum mechanics to solve very difficult problems at speeds faster than ever before! I will talk more about what quantum computing is, its potential applications, and the challenges.
To understand quantum computing you first need to understand classic computing, which I’ll quickly explain. Classic computers rely on bits, which can be either 0 or 1, and these bits are used to store information and perform complex calculations. On the other hand, quantum computers use quantum bits, qubits for short, which can exist in not only 0 or 1 but multiple states at the same time. Qubits are able to exist in multiple states simultaneously because of superposition. Quantum entanglement is another phenomenon that qubits experience, where 2 qubits can be interdependent, meaning one qubit can influence the state of another one, no matter how far they are! These principles let quantum computers process a vast amount of data at the same time, which makes them extremely powerful when it comes to complex tasks that classical computers might not be able to perform so fast. For example, while a classical computer might check each possible solution individually, quantum computers are able to process multiple solutions at once which immensely speeds up the process.
Quantum computers can be used in multiple different areas. One of these is cryptography; because of their quick computational nature they can be used to break some of the most commonly used encryption methods, for which there are quantum-resistant algorithms being developed. It can also be used in artificial intelligence, improving upon the machine learning algorithms, and enabling faster data processing which could greatly impact fields of natural language processing, image recognition, and autonomous systems.
Although this sounds amazing, there are multiple challenges that we face with scalability, cost of infrastructure, and accessibility. Which is one of the reasons why quantum computing is not currently used to the best of its potential.
In conclusion, quantum computing does hold a lot of promise, but there are big issues to overcome. It is a highly anticipated technological advancement, and as research and development progress, we could be in a new era of innovation. Not only would this transform industries but also help in improving our understanding behind the physics of the universe!





